Derivative of ln(x^23x1) Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem We hope it will be very helpful for you and it will help you to understand the solving processDerivative of Ln(x2) Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem We hope it will be very helpful for you and it will help you to understand the solving processCalculus Find the Derivative d/dx y = natural log of e^ (x^2) y = ln (ex2) y = ln ( e x 2) Use logarithm rules to move x2 x 2 out of the exponent d dx x2ln(e) d d x x 2 ln ( e) The natural logarithm of e e is 1 1 d dx x2 ⋅1 d d x x 2 ⋅ 1 Multiply x2 x 2 by 1 1 d dx x2 d d x x 2
Find The First Derivative Of Y Y Ln X Squareroot Chegg Com
Derivative of ln(x^2+y^2)^1/2
Derivative of ln(x^2+y^2)^1/2-Derivative of ln(xsqrt(1x^2)), Full playlist https//wwwyoutubecom/playlist?list=PLj7p5OoL6vGzLwDjpT3gOA1K3RwUo8jDIf you enjoy my videos, then you canI am trying to find the derivative of $\ln(x\sqrt{x^21})$ but I can not get what the book gets I get $$\frac{1}{x \sqrt{x^21}} \cdot \sqrt{x^21} x\cdot\frac{1}{2}(x^21)^\frac{1}{2}\cdot2x$$
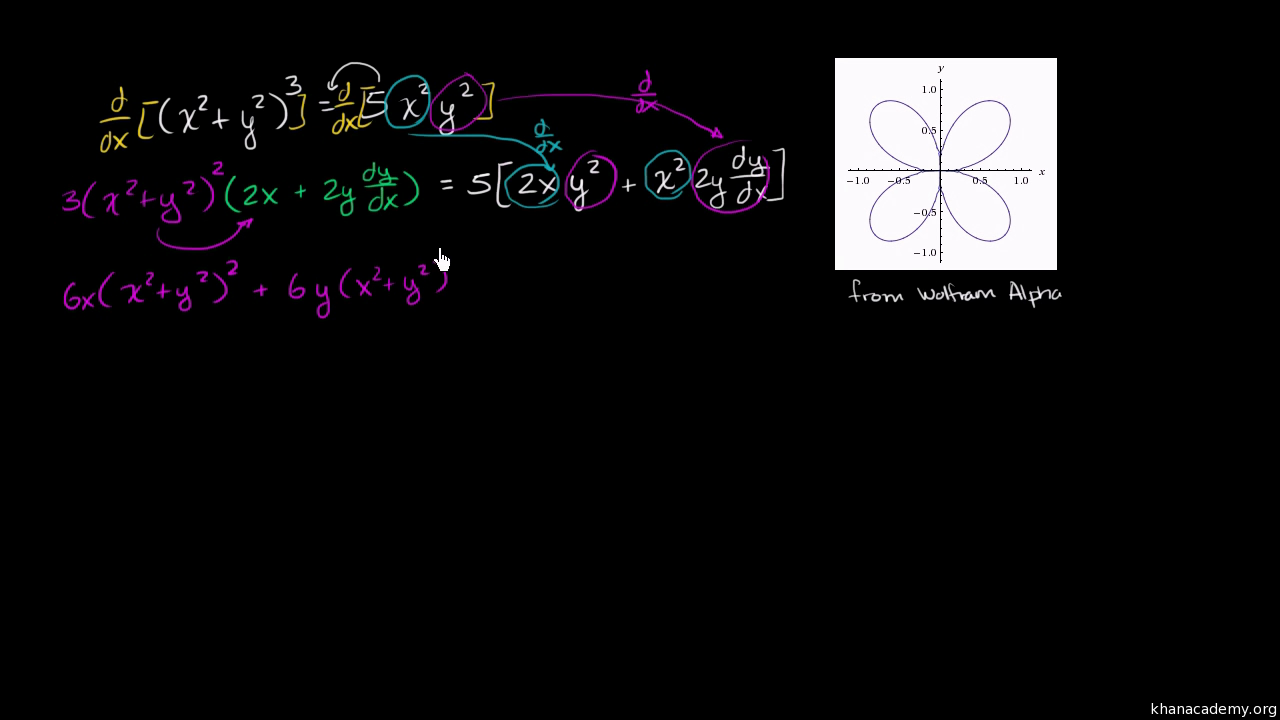



Implicit Differentiation Advanced Example Video Khan Academy
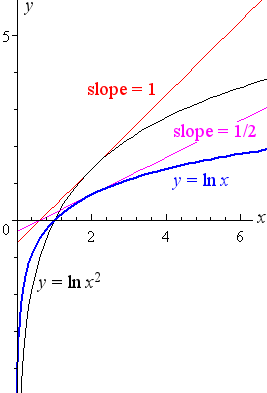
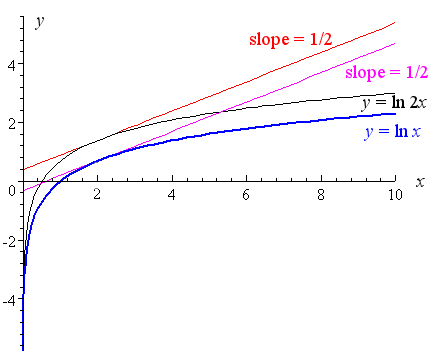
Leaving us with the derivative of ln x, which is 1/x The constant 2 comes out of the differentiation The 2 multiplied by 1/x is written as 2/x Step 3 Simplify Thus, the derivative of ln x2 is 2/x Note this result agrees with the plots of tangent lines for both positive and negative xUseful resource https//amznto/2RvJIyVImage Page http//calculuscoachescom/indexphp/home/derivativeoflnx2/The Derivative Calculator supports computing first, second, , fifth derivatives as well as differentiating functions with many variables (partial derivatives), implicit differentiation and calculating roots/zeros You can also check your answers!
Answer and Explanation We have f(x,y,z) = (x2y2z2)−1/2lnxyz f ( x, y, z) = ( x 2 y 2 z 2) − 1 / 2 ln x y z We apply the del operator to the function to get the gradient ∇fDerivative of y=\ln(\sqrt{1x^{2}}) zs Related Symbolab blog posts My Notebook, the Symbolab way Math notebooks have been around for hundreds of years You write down problems, solutions and notes to go backDerivative of ln(25x^2) Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem We hope it will be very helpful for you and it will help you to understand the solving process
This video illustrates the tangent line to the 3D surface to illustrate the meaning of the value of a directional derivativewebsite http//mathispower4ucomGet stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!Interactive graphs/plots help visualize and better understand the functions



Implicit Differentiation Advanced Example Video Khan Academy




How To Find Dy Dx When Ln Xy X Y Quora
Question Find The Derivative Of The Function Y = X^2 Ln X^2 2(x Ln X) 2x^2(1 Ln X^2)/x^2 2x(1 Ln X^2) 2x Ln X^2 This problem has been solved! `` ==> The derivative of `lnx/x^2` is `f'(x)= (12lnx) What is the derivative of y = x^(ln x) where ln x is the natural logarithm of x 1 EducatorRelated Pages Natural Logarithm Logarithmic Functions Derivative Rules Calculus Lessons Natural Log (ln) The Natural Log is the logarithm to the base e, where e is an irrational constant approximately equal to The natural logarithm is usually written ln(x) or log e (x) The natural log is the inverse function of the exponential function




The Derivative Of Lnx And Examples Mathbootcamps



Find The First Derivative Of Y Y Ln X Squareroot Chegg Com
Transcribed image text a Find the derivative of f(x, y) = ln(4 x^2 y^2 at P(1, 2) in the direction of v = 2i j b If you are located on the surface f(x, y) = ln(4 x^2 y^2) at the point (1, 2, ln 9), in which direction should you move in order to ascent on the surface at the max rate?Answer to Find the first derivative of y= ln (x^{5/2} square root{1x^{10}}) By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutions toDifferentiate using the Power Rule which states that d d x x n d d x x n is n x n − 1 n x n 1 where n = 2 n = 2 Since y 2 y 2 is constant with respect to x x, the derivative of y 2 y 2 with respect to x x is 0 0 Combine fractions Tap for more steps Add 2 x 2 x and 0 0 Combine 2 2 and 1 x 2 y 2 1 x 2 y 2



5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function
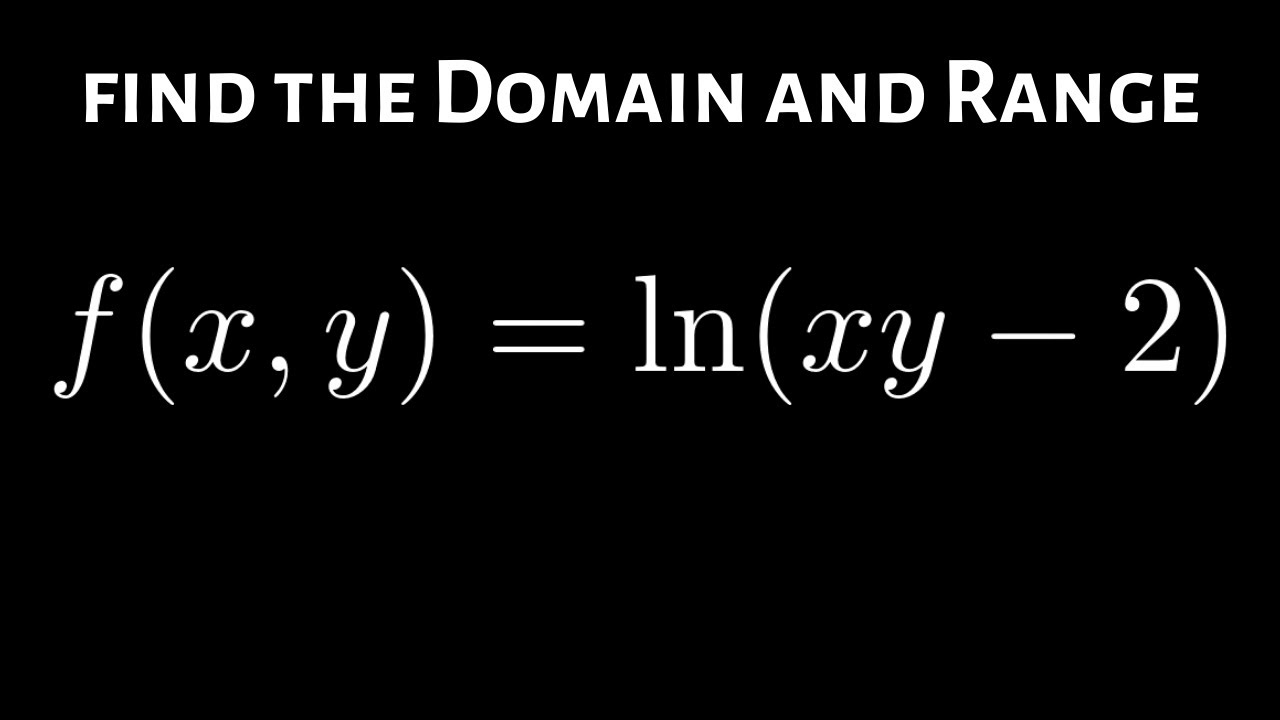



How To Find The Domain And Range Of F X Y Ln Xy 2 Youtube
Derivative x^2(xy)^2 = x^2y^2 Natural Language;The natural logarithm of a number is its logarithm to the base of the mathematical constant e, which is an irrational and transcendental number approximately equal to 2718 281 8 459The natural logarithm of x is generally written as ln x, log e x, or sometimes, if the base e is implicit, simply log x Parentheses are sometimes added for clarity, giving ln(x), log e (x), or log(x)Answer to Let y = ln (x^2 y^2) Determine the derivative y '




Calculating The Derivative Of Ln X 2 Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Formula For Nth Derivative Of Logarithmic Function Ln X 1 Youtube
Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!Let {eq}y=x^x {/eq} Compute the derivative {eq}y'(\frac{1}{2}) {/eq} a {eq}1\ln 2 {/eq} b {eq}\frac{1}{\sqrt 2} {/eq} c {eq}\frac{1}{4} {/eq}Derivatives Derivative Applications Limits Integrals Integral Applications Integral Approximation Series ODE Multivariable Calculus Laplace Transform Taylor/Maclaurin Series Fourier Series \frac{\partial}{\partial y}(y^{2}\ln(1x^{2}y^{2})) en Related Symbolab blog posts Practice, practice, practice Math can be an intimidating subject
.gif)



Calculus Differentials And Integrals




Name Find The Power Series Expansion Of Y Ln X At Chegg Com
Question Find the derivative of z = x ln y at the point (1, 2) in the direction making an angle of 30 with the positive xaxis This question hasn't been solved yetDerivative of ln(x*sqrt(x^2)), derivative of ln(xsqrt(x^21)), If you enjoy my videos, then you can click here to subscribe https//wwwyoutubecom/blackpeDerivative of (x^2*y^2)^1 Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem We hope it will be very helpful for you and it will help you to understand the solving process
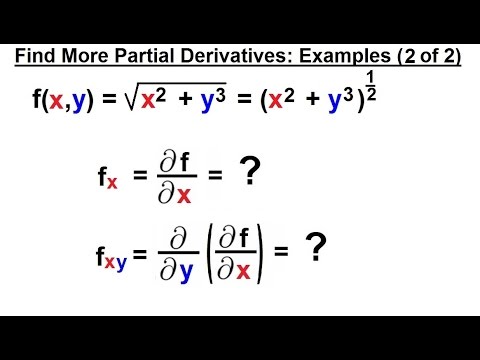



Calculus 3 Partial Derivative 14 Of 30 Find More Partial Derivatives Example 2 Of 2 Youtube




Worked Example Derivative Of Ln X Using The Chain Rule Video Khan Academy
Using the chain rule, the derivative of ln^2x is 2ln (x)/x Finally, just a note on syntax and notation ln^2x is sometimes written in the forms below (with the derivative as per the calculations above) Just be aware that not all of the forms below are mathematically correct ln 2 x Derivative of ln 2 x = 2ln (x)/xExtended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, musicTangent of x^2xyy^2=1, (2,3) \square!




Compute The Derivative Of Y Ln X 4 X 3 First Chegg Com



Madasmaths Com Archive Maths Booklets Standard Topics Various Differentiation Ii Exam Questions Pdf
Derivative of ln (x1) \square!Derivative of ln(11/x), two ways, calculus 1 derivative example, how to take the derivative, logarithmic derivative, blackpenredpen, math for fun, https//tThe first derivative of mathz/math with respect to mathx/math is math\frac {\partial z}{\partial x}=\frac {2x}{x^2y^2}/math The second derivative is




Ppt Section 3 5 Find The Derivative Of G X X 2 Ln X You Will Need To Use The Product Rule Powerpoint Presentation Id



How Do You Determine Whether The Function F X Ln X 2 7 Is Concave Up Or Concave Down And Its Intervals Socratic
4618 views around the world You can reuse this answer Creative Commons LicenseLearn how to solve implicit differentiation problems step by step online Find the implicit derivative (d/dx)(x^2y^2=1) Apply implicit differentiation by taking the derivative of both sides of the equation with respect to the differentiation variable The derivative of the constant function (1) is equal to zero The derivative of a sum of two functions is the sum of the derivatives of eachSee the answer Let f (x, y, z) = sin (xyz) ln (x 2 3y 2 ) Find the directional derivative of f (x, y, z), as you leave the point (1, 1, π) heading in the direction of the point (−3, 1, 3 π) Show transcribed image text



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation




Evaluate The Indicated Derivatives A Partial Chegg Com
At the point (1, 0) y '(1) = By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystepFind the derivative of the following via implicit differentiation d/dx(y) = d/dx(tan^(1)(x^3)^2) Using the chain rule, d/dx(y) = ( dy(u))/( du) ( du)/( dx), where uMathy=x^{1/2}/math math\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{1}{2}x^{1/2}/math math\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{1}{2x^{1/2}}/math math\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{x}}/math
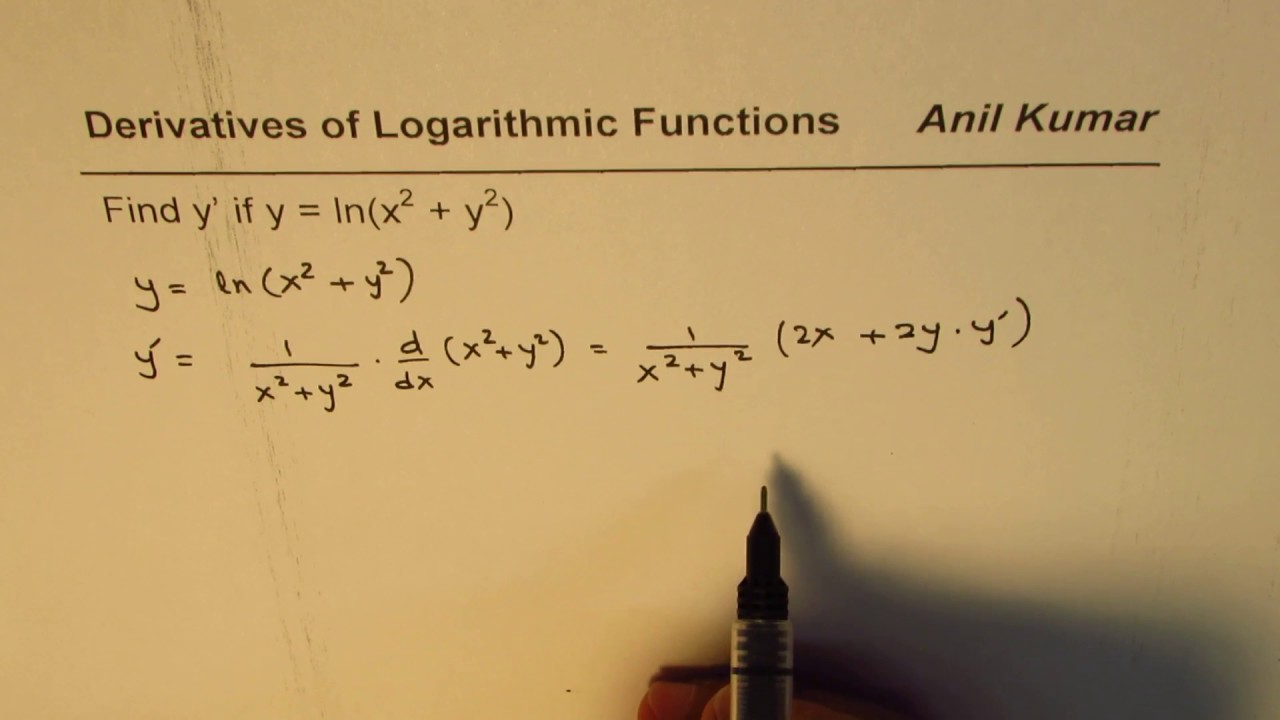



Implicit Derivation Of Logarithmic Function Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Youtube
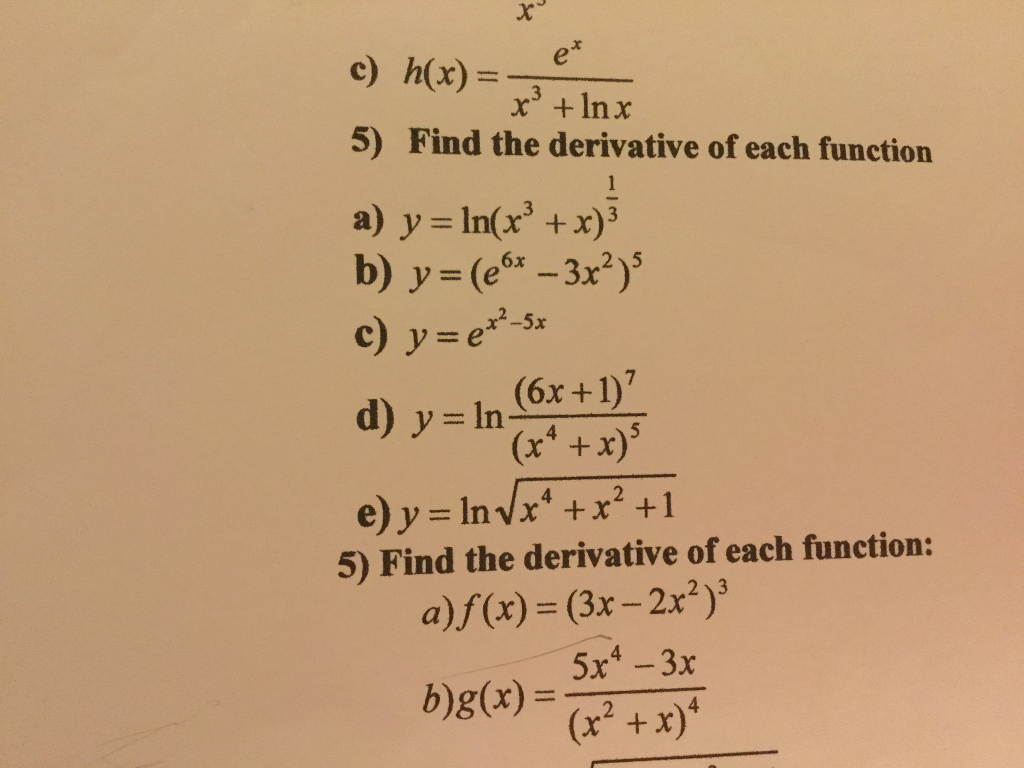



Find The Derivative Of Each Function Y Ln X 3 Chegg Com
The derivative of a function multiplied by a constant (2) is equal to the constant times the derivative of the function The derivative of the natural logarithm of a function is equal to the derivative of the function divided by that function If f(x)=ln\a (where a is a function of x), then \displaystyle f'(x)=\frac{a'}{a} Derivative of y = ln u (where u is a function of x) Unfortunately, we can only use the logarithm laws to help us in a limited number of logarithm differentiation question types Most often, we need to find the derivative of a logarithm of some function of xFor example, we may need to find the derivative of y = 2 ln (3x 2 − 1) We need the following formula to solve suchThis problem has been solved!



5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function
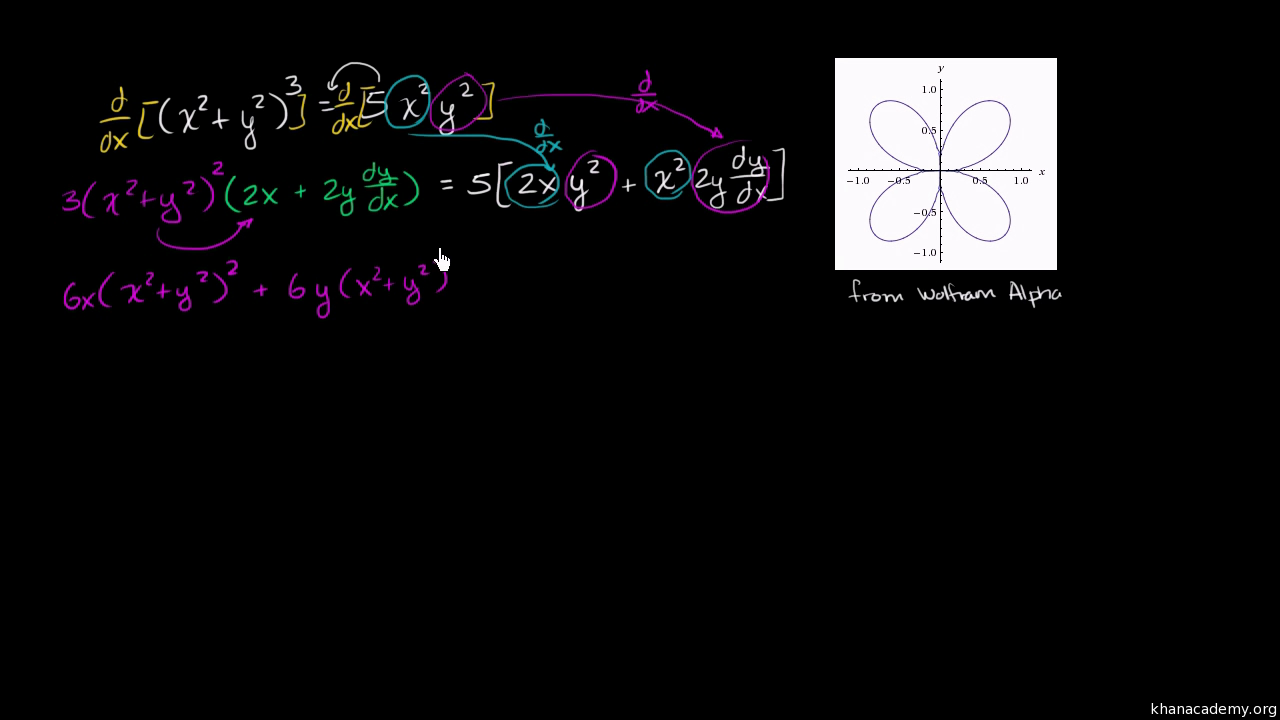



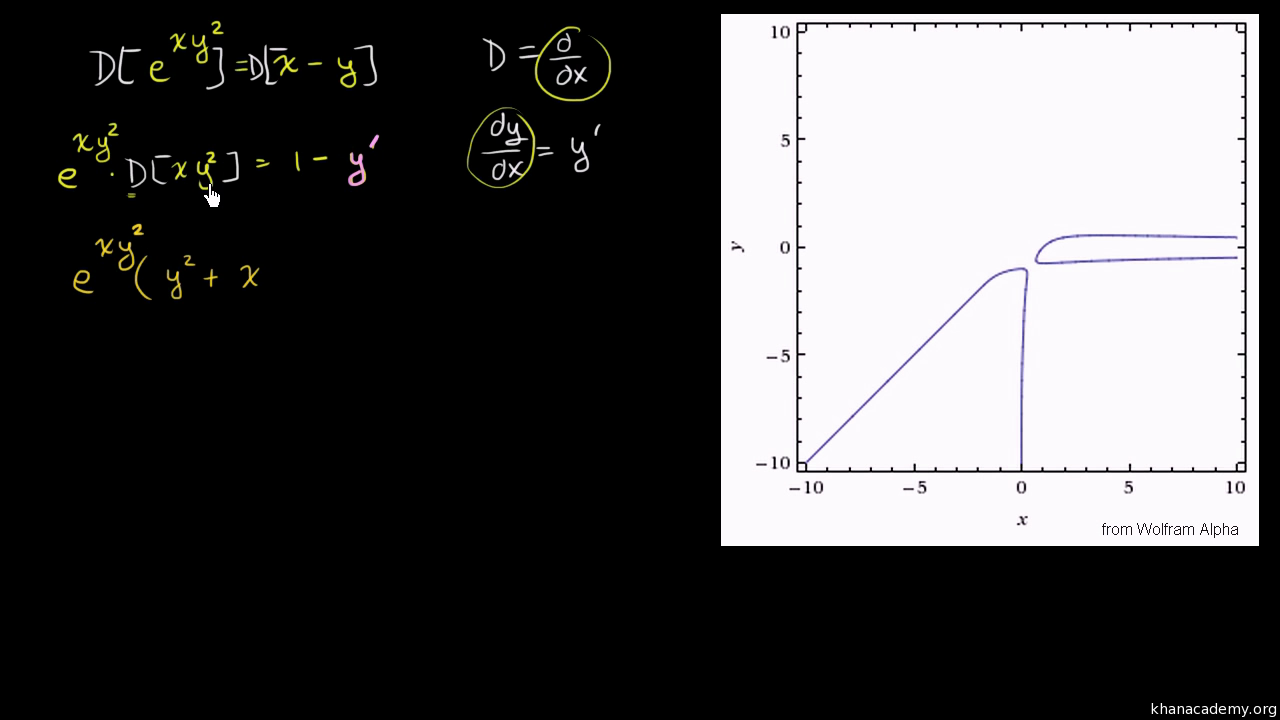
Implicit Differentiation Advanced Example Video Khan Academy
You can see that along the line y = x that will simplify to y ′ = 1 as it should Note that the point ( 4, 2) is a solution to the original equation The derivative there is y ′ = 1 / 2 − log 2 2 − log 4 which is about − 0314 which looks about right based on the graph above 1 Answer1 Active Oldest Votes 1 It is correct To justify your feeling, you can apply the chain rule to the maps g x ↦ x 2 y 2 (where y is fixed) and f x ↦ ln xWe use the Chain Rule Our function has the shape $\ln(g(x))$, where $g(x)=x\sqrt{x^2a^2}$ The derivative is therefore $\frac{g'(x)}{g(x)}$ We have $$g'(x)=1\frac{x}{\sqrt{x^2a^2}}=\frac{\sqrt{x^2a^2}x}{\sqrt{x^2a^2}}$$ When we divide by $x\sqrt{x^2a^2}$ and simplify, we get $\frac{1}{\sqrt{x^2a^2}}$




The Derivative Of Lnx And Examples Mathbootcamps




Let F X 1 X Ln X Sqrt X 2 1 Sqrt 1 X 2 A N D H X F X F 2 X F 3 X Dot Then
Find the derivative of z = x ln y at the point (1, 2) in the direction making an angle of 30 with the positive xaxis;Derivative of ln(x^2) Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem We hope it will be very helpful for you and it will help you to understand the solving processDerivatives Derivative Applications Limits Integrals Integral Applications Integral Approximation Series ODE Multivariable Calculus Laplace Transform Taylor/Maclaurin {1}{2}\ln(x^{2}y^{2})) en Related Symbolab blog posts My Notebook, the Symbolab way Math notebooks have been around for hundreds of years You write down problems



How Do You Find The Derivative For F X X 9 X 2 6x 1 Socratic



5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high 94% (17 ratings) When you take the gradient of a function you will get a vectorExample find the derivative of f(x) = ln(1 x)(1 x 2) 2 (1 x 3) 3 Solution The last thing that we want to do is to use the product rule and chain rule multiple timesFind the gradient of f(x,y)=ln(x^2y^2) Expert Answer Who are the experts?




Help Please For 1 2 6 Find The First Order Partial Chegg Com



How Do You Find The First And Second Derivative Of Lnx 3 Socratic




Review 7 2 Find The Derivative 1 F X Ln 3x 4 X F X Ln 1 X 1 X2 2 1 X3 3 Ln 1 X Ln 1 X 2 2 Ln 1 X Ppt Download



Finding The Derivative Of Ln X X How To Steps Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function




Show That Z Ln X 2 Y 2 2 Tan 1 Y X Satisfies The Laplaces S Equation Mathematics Stack Exchange



What Is The Nth Derivative Of Math X 2 Ln 3 X Math Quora



Differential Equations Separation Of Variables Ppt Download




Find The Derivative Y Ln X X 6 Y E X 5 Lnx Chegg Com




Derivative Of F X Ln Ln X 2 1 Youtube




Find Y For Ln X Y Arctan Xy Mathematics Stack Exchange




Find Y X If It Satisfies The Following Differential Equation Dy Dx X Y 2 And Given That Y 1 1 A Ln 1 X Y 1 X Y 2 X 1 B Ln 2 Y 2 X X Y 1 C Ln 1 X Y 1 X Y 2 X 1 D 1 2ln 1 X Y 1 X Y Ln X 0




Show That Z Ln X 2 Y 2 2 Tan 1 Y X Satisfies The Laplaces S Equation Mathematics Stack Exchange
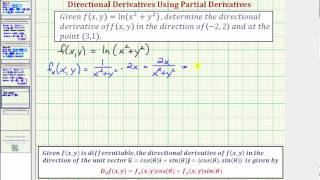



Ex 3 Find A Value Of A Directional Derivative F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Youtube




Review 7 2 Find The Derivative 1 F X Ln 3x 4 X F X Ln 1 X 1 X2 2 1 X3 3 Ln 1 X Ln 1 X 2 2 Ln 1 X Ppt Download



What Is The Differentiation Of Ln Sinx Quora



Proof The Derivative Of Ln X Is 1 X Video Khan Academy




Derivative Of Ln X Lnx 2 1 Lnx More
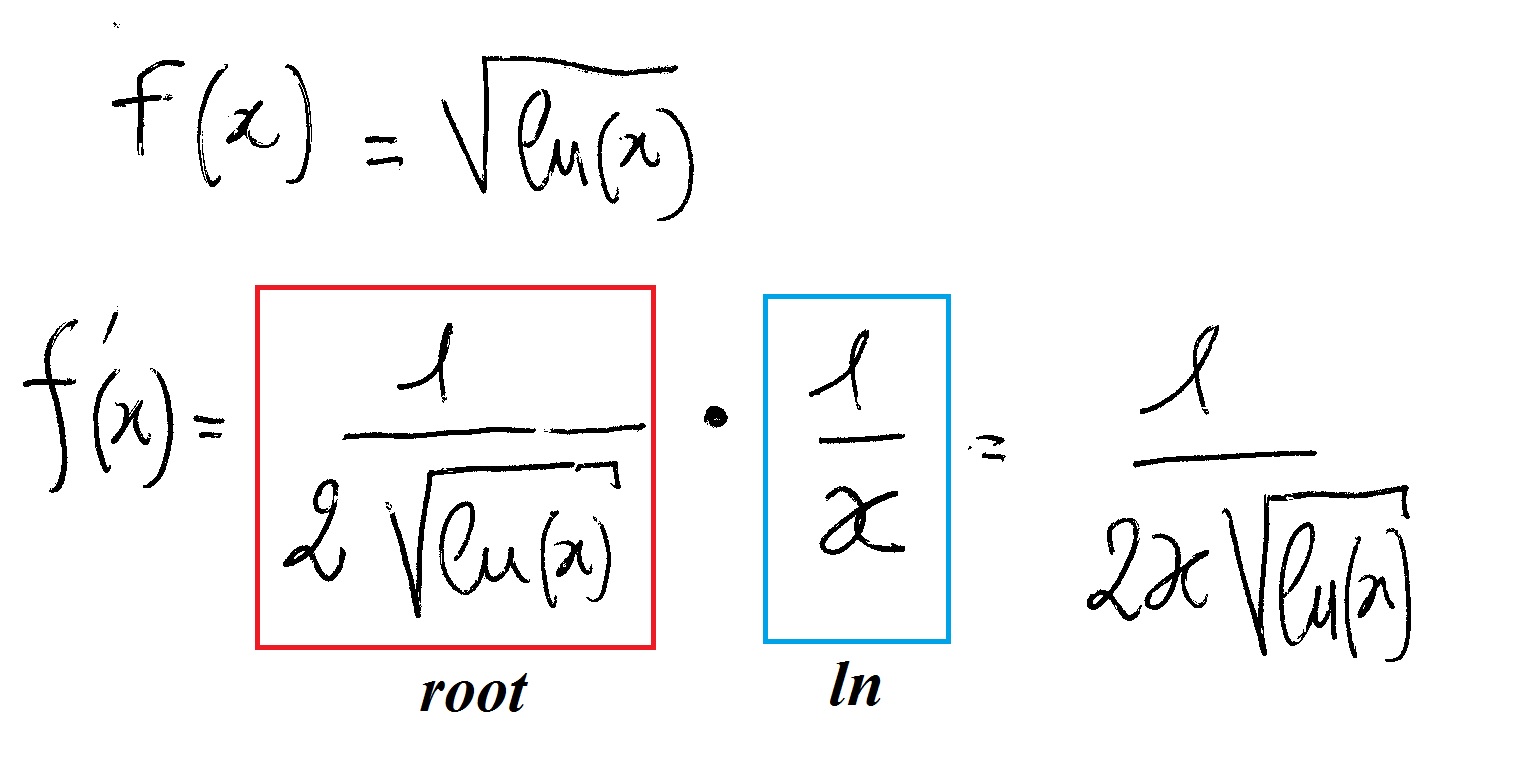



What Is The Derivative Of The Sqrt Ln X Socratic
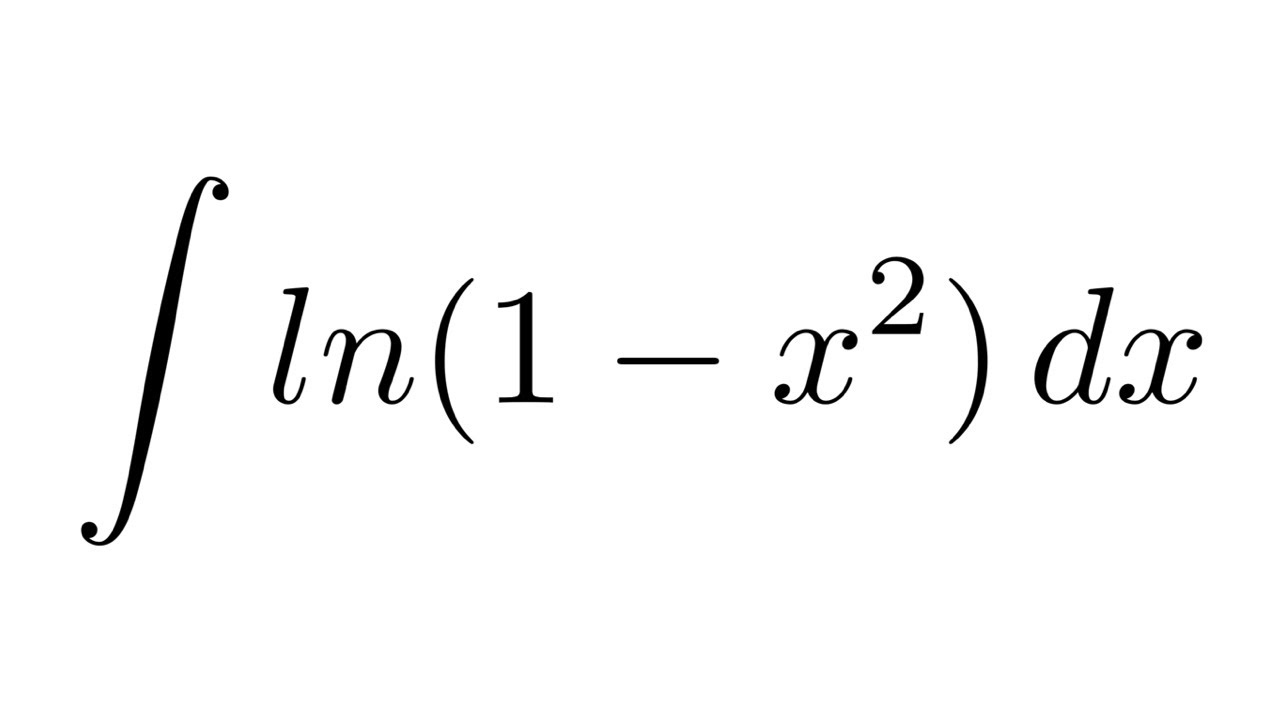



Integral Of Ln 1 X 2 By Parts Youtube




Calculating The Derivative Of Ln X 2 Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Derivative Calculator Wolfram Alpha




Section 3 5 Find The Derivative Of G X X 2 Ln X Ppt Video Online Download
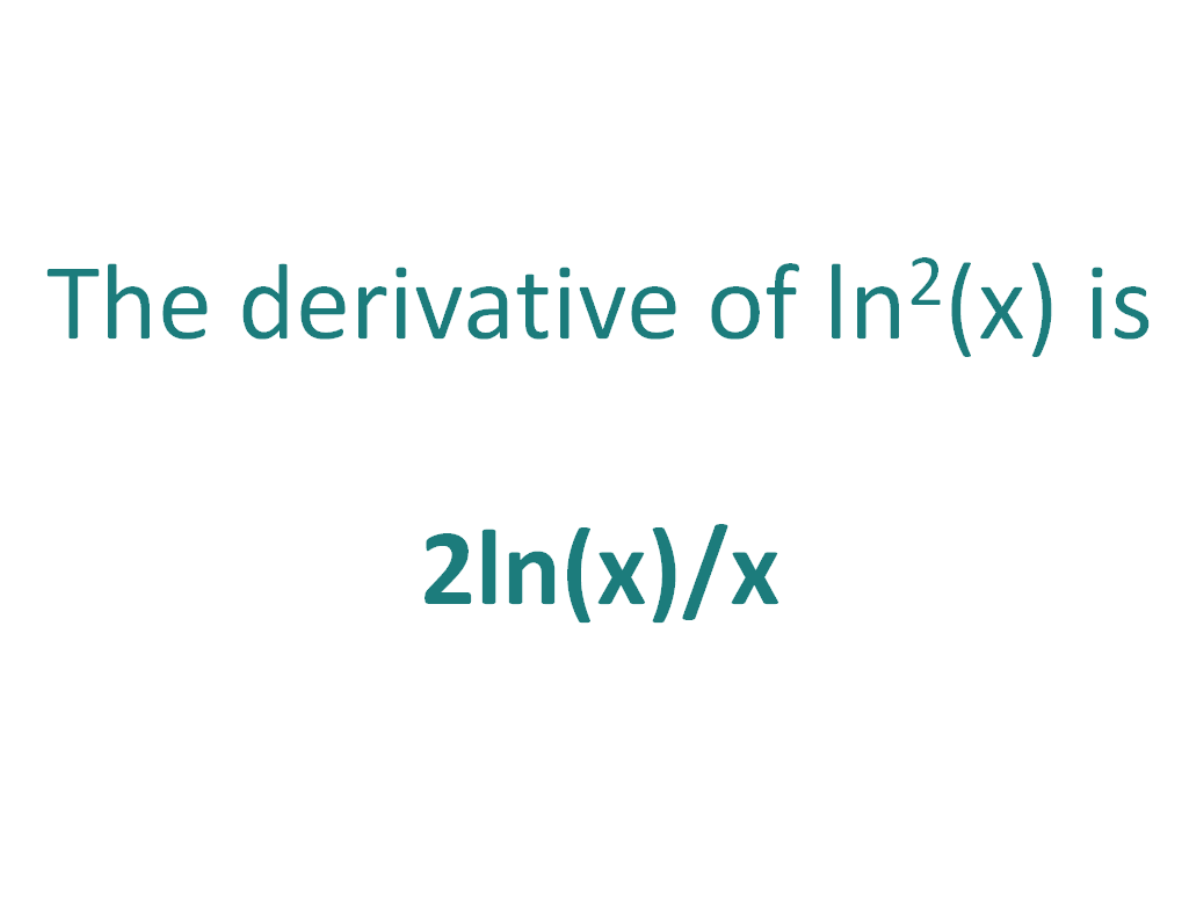



The Derivative Of Ln 2 X Derivativeit




Calculating The Derivative Of Ln X 2 Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Derivative Of Ln X Youtube



Partial Derivatives




What Is The Differentiation Of X 2 Quora
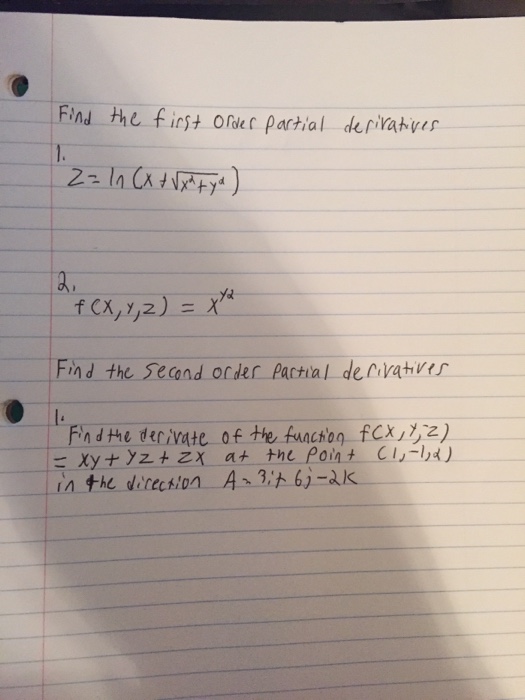



Find The First Order Partial Derivatives Z Ln X Chegg Com




Solving The Derivative Of Ln Sqrt X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
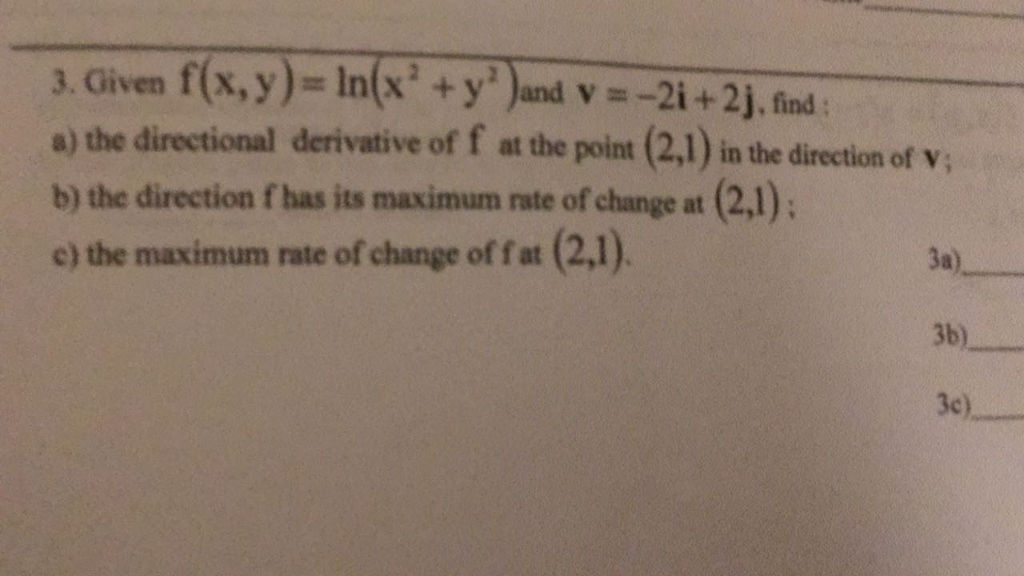



Given F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 And V 2i 2j Find Chegg Com



How Do You Find The Derivative Of Y X Ln X Sin X Socratic
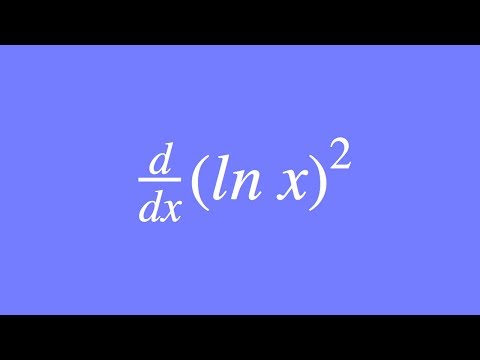



How To Differentiate Ln X 2 Using The Chain Rule Youtube
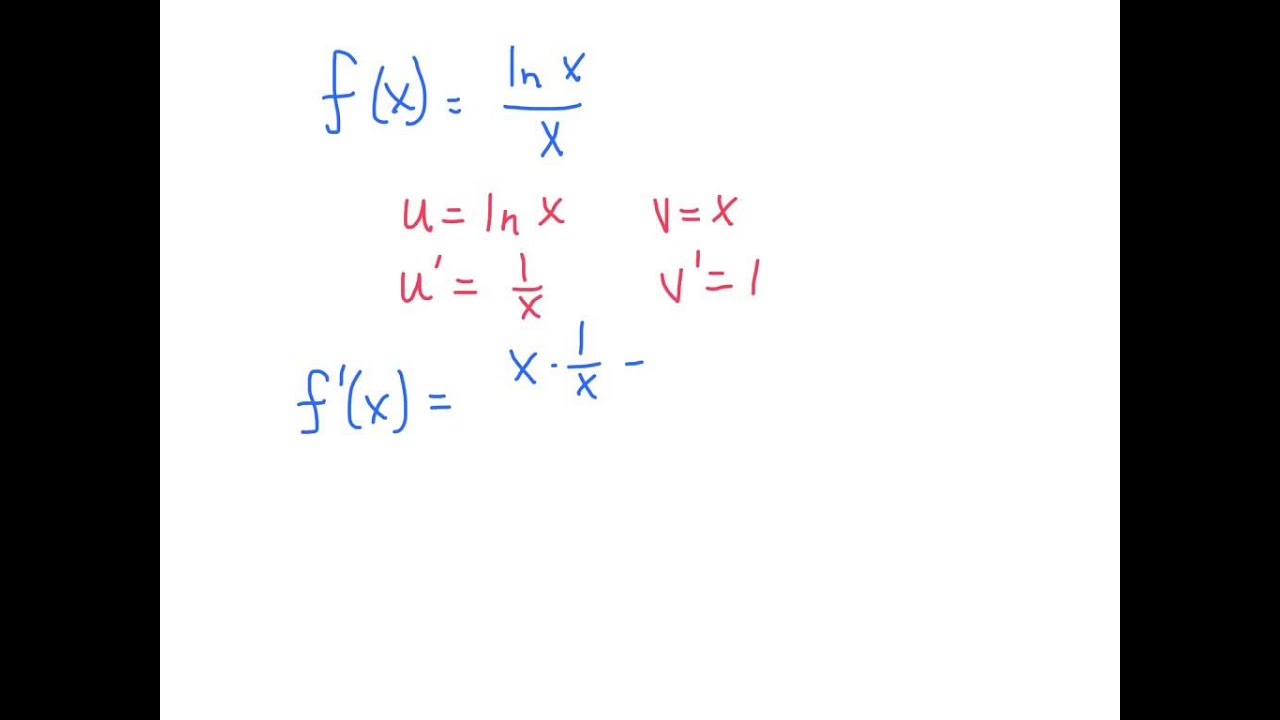



Derivative Of Ln X X Youtube



Www Ualberta Ca Rjia Math214 Hwks Sol8 Pdf



Derivative 1 2 1 2 Ln X 1 X 1 Arctanx Mathskey Com




Derivative Of Ln X From Derivative Of 𝑒ˣ And Implicit Differentiation Video Khan Academy
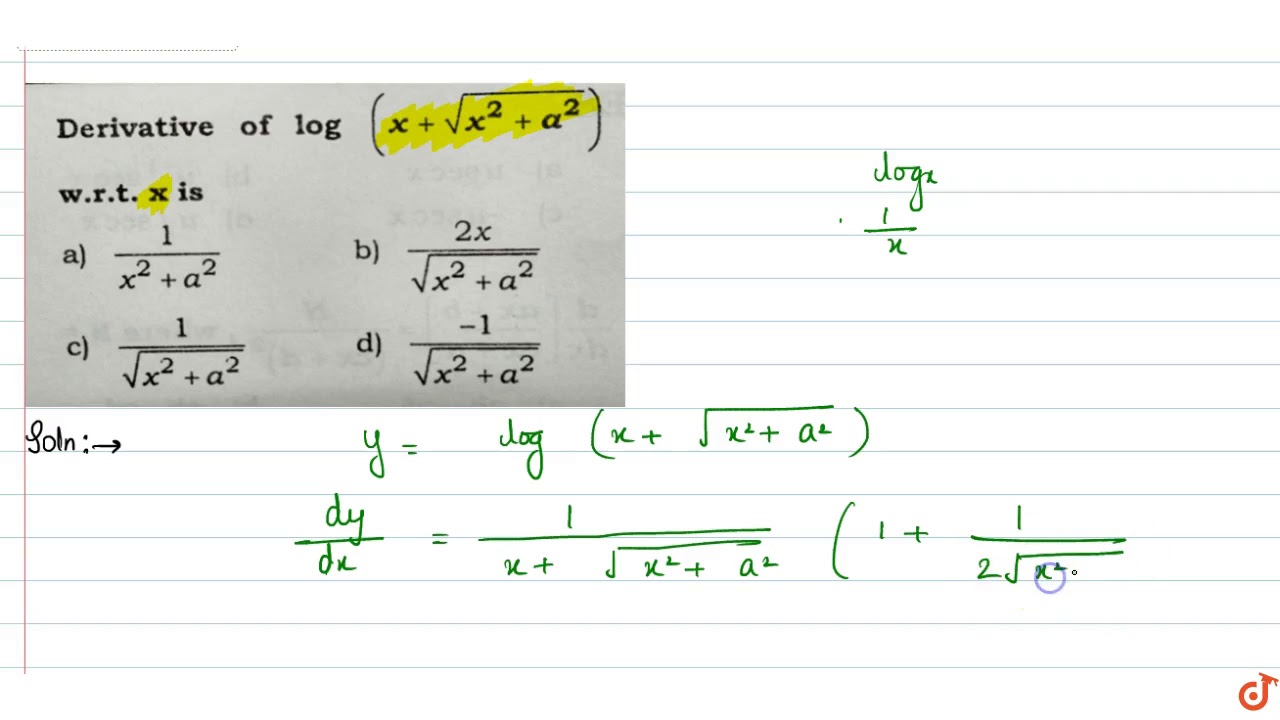



Derivative Of Log X Sqrt X 2 A 2 W R T X Is Youtube




Derivative Of Ln X Natural Logarithm More
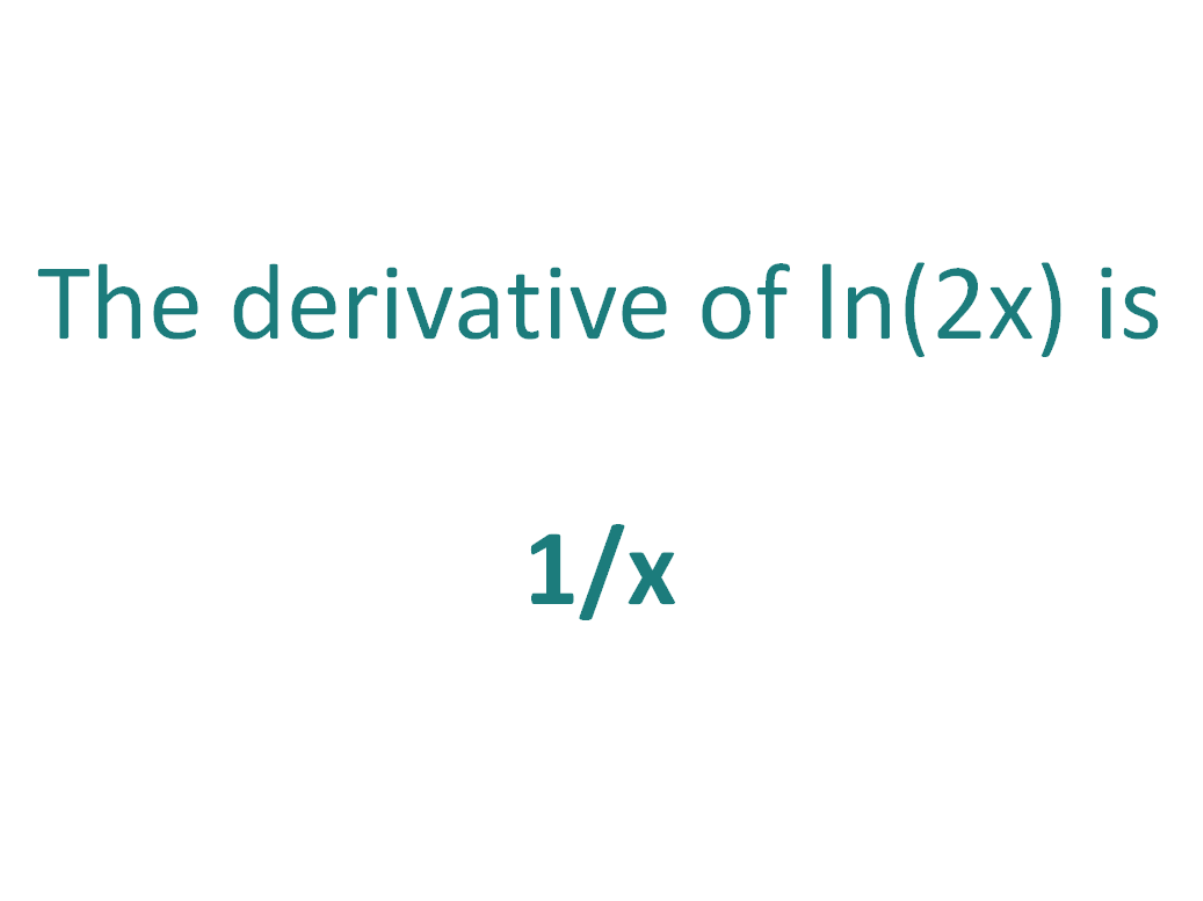



The Derivative Of Ln 2x Derivativeit



5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function
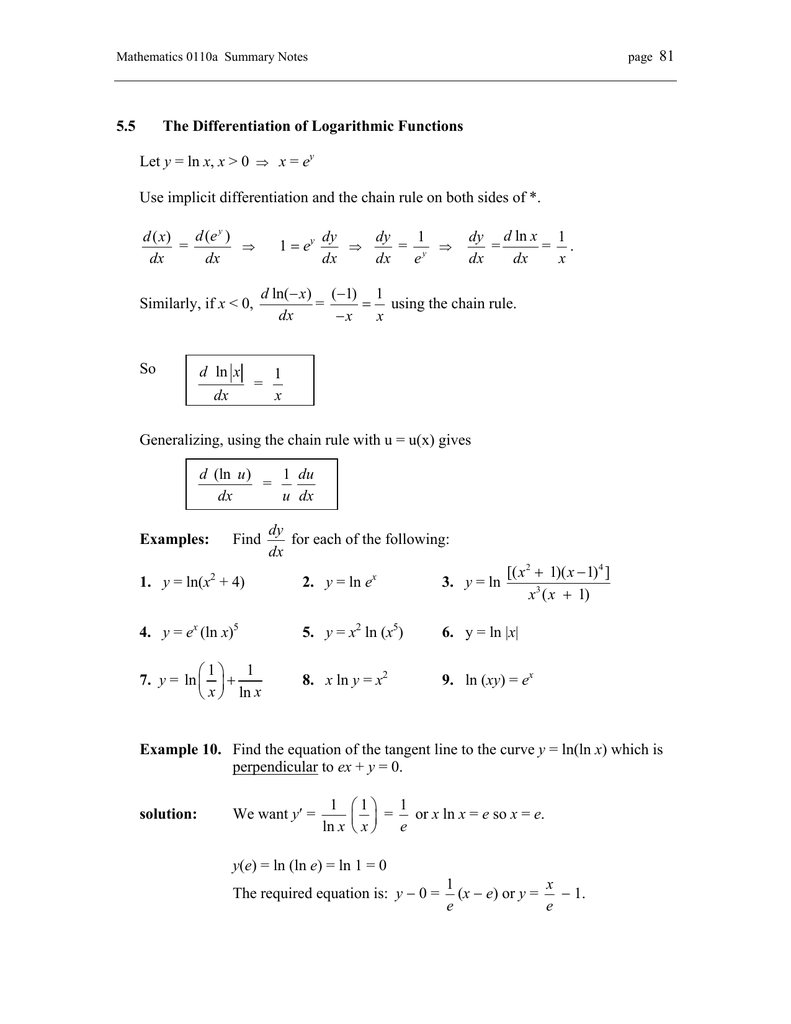



5 5 The Differentiation Of Logarithmic Functions Let Y Ln X X 0




Consider The Function F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 3 Compute The Partial Derivatives Of The First And Second Order Mathematics Stack Exchange



Q Tbn And9gcq2d7kmfugm3bw Yamxgmz0pjqw30uksgoo Pwbcds44idetqvc Usqp Cau
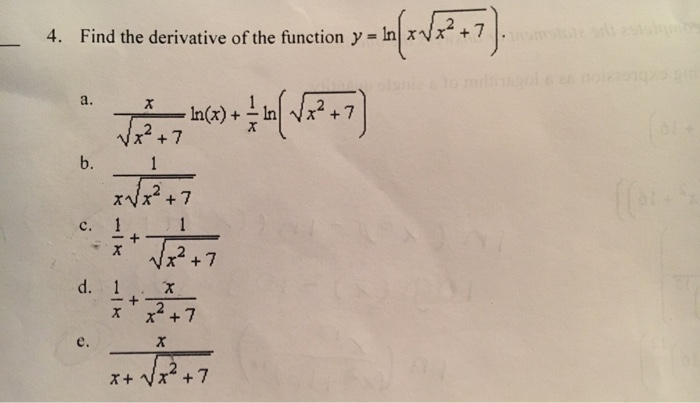



Find The Derivative Of The Function Y Ln X Chegg Com




Logarithmic Derivatives Y Ln X 8 1 3 2 Youtube
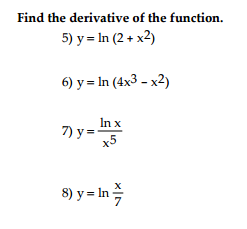



Find The Derivative Of The Function 5 Y Ln 2 Chegg Com




Lesson 16 Derivatives Of Logarithmic And Exponential Functions
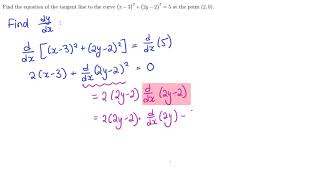



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation




Find 1st And 2nd Derivatives For Y Ln X 2 5x Youtube



3
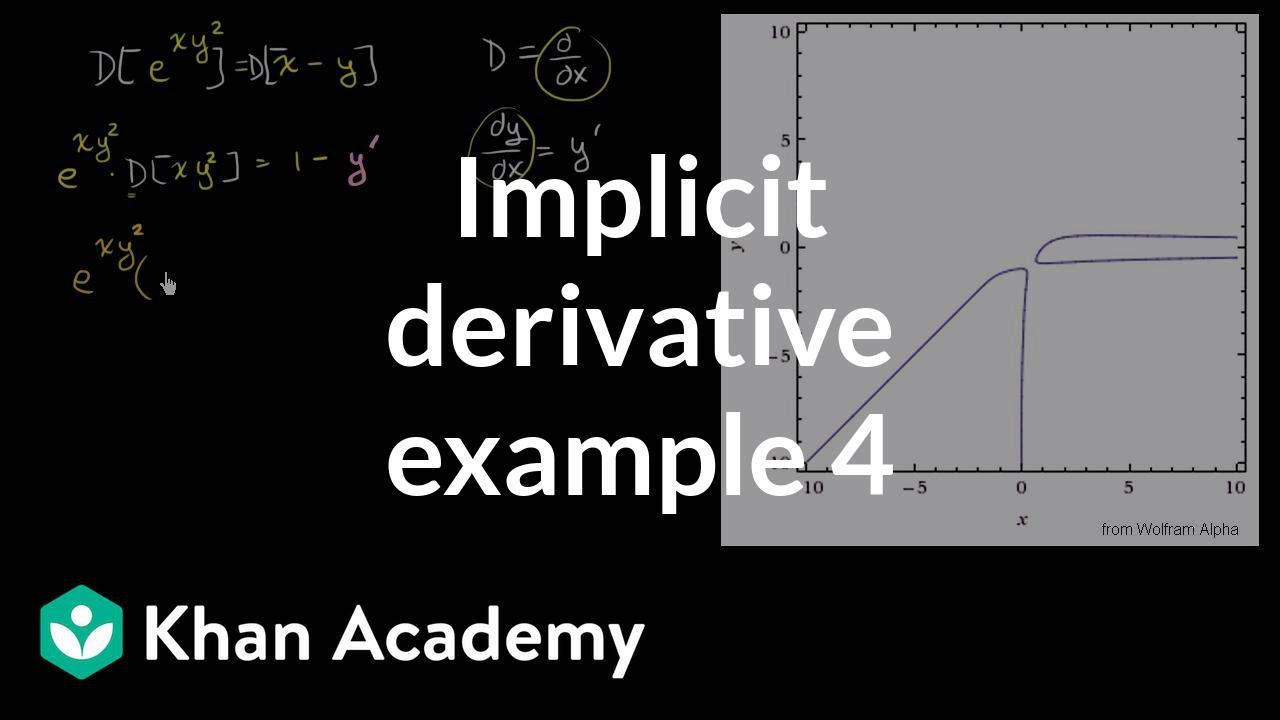



Implicit Differentiation Advanced Example Video Khan Academy




How Do You Find The First And Second Derivative Of Ln X X 2 1 1 2 Socratic
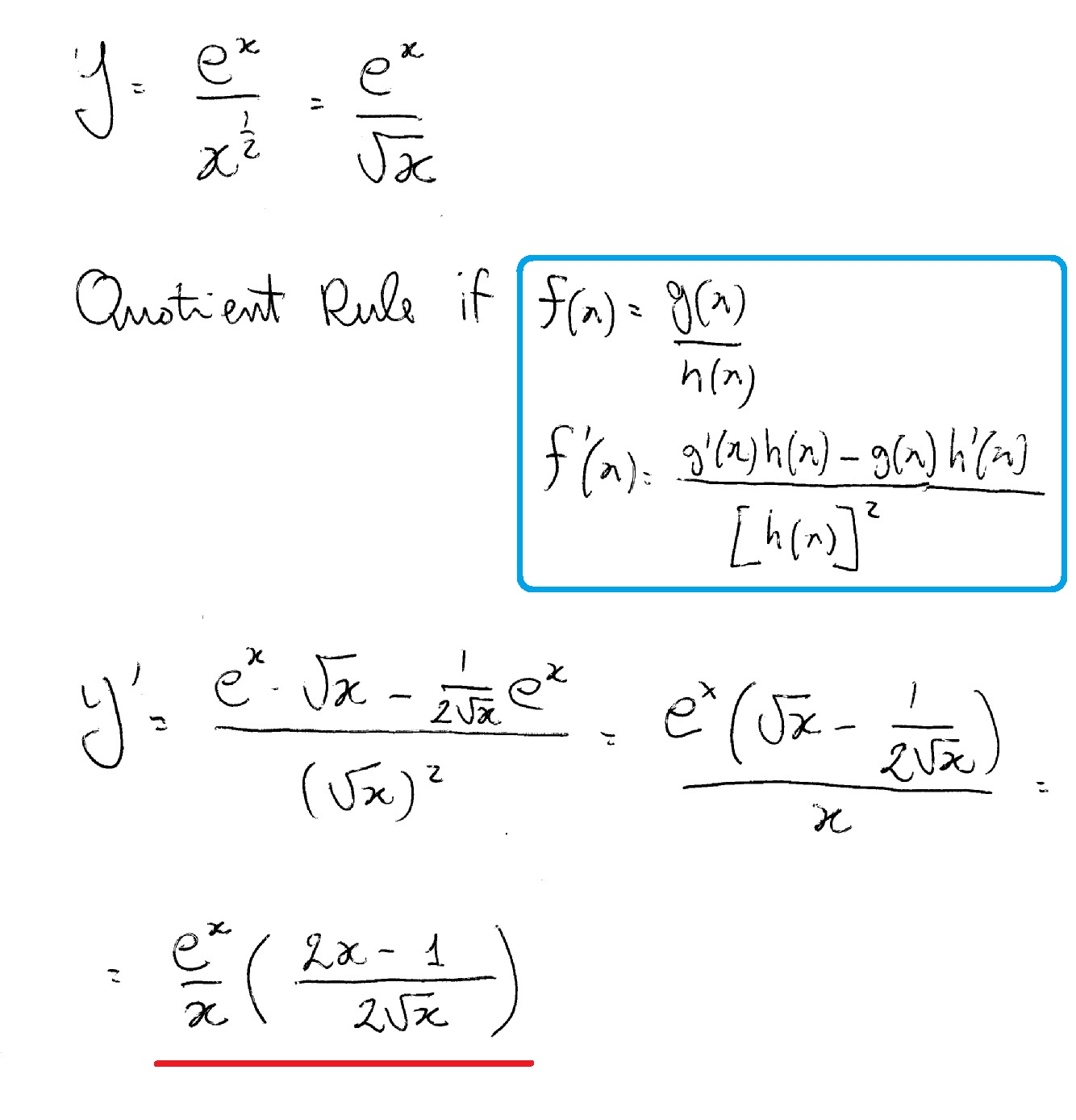



How Do You Find The Derivative Of Y E X X 1 2 Using The Quotient Rule Socratic
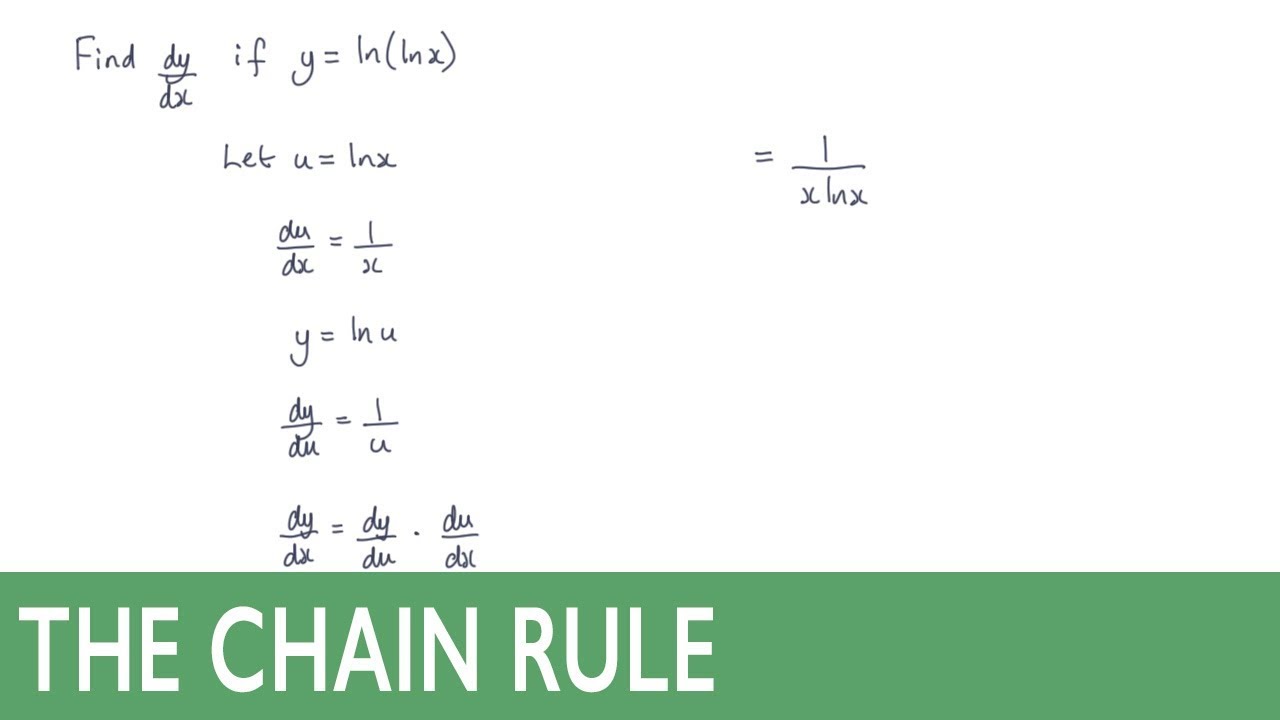



How To Differentiate Y Ln Lnx Using The Chain Rule Youtube
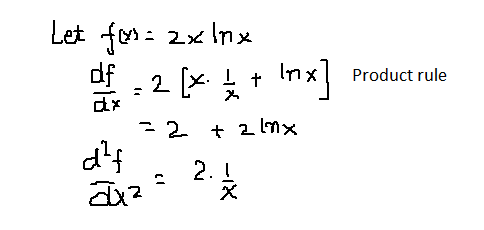



How Do You Find The First And Second Derivative Of 2x Ln X Socratic



1
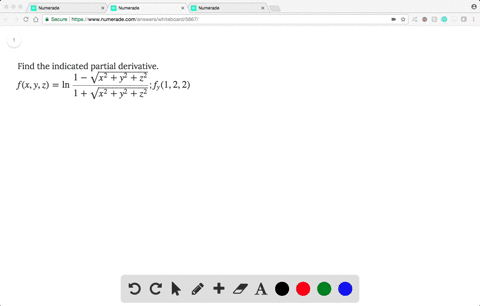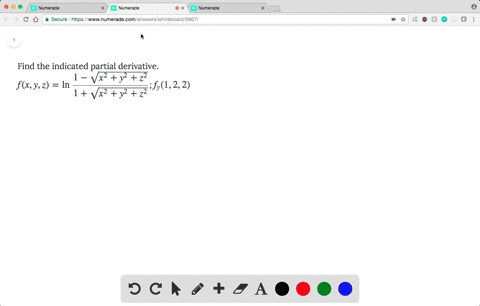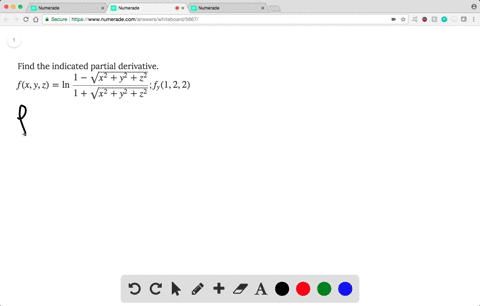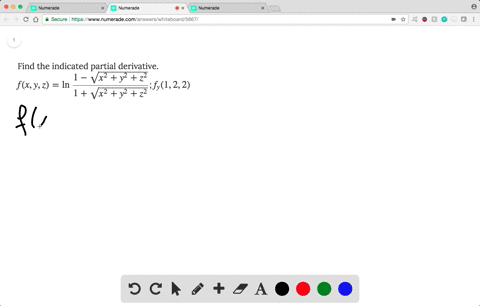



Solved Find The Indicated Partial Derivative F X Y Z Ln Dfrac 1 Sqrt X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1 Sqrt X 2 Y 2




Derivative Of Ln X Natural Logarithm More
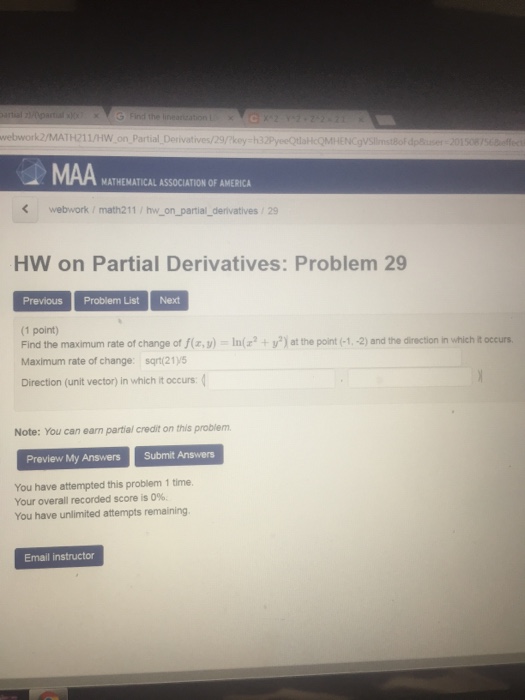



Find The Maximum Rate Of Change Of F X Y Ln X 2 Chegg Com



Partial Derivative Of F X Y Xy X 2 Y 2 With Quotient Rule Youtube



Search Q Product Rule Tbm Isch



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation




How Do You Find The Derivatives Of Z Ln Y 4 1 2 Y 1 3 Socratic




Find The Derivative Of The Function At P 0 In The Chegg Com




Let Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Determine The Derivative Y At Chegg Com



Derivative Calculator With Steps
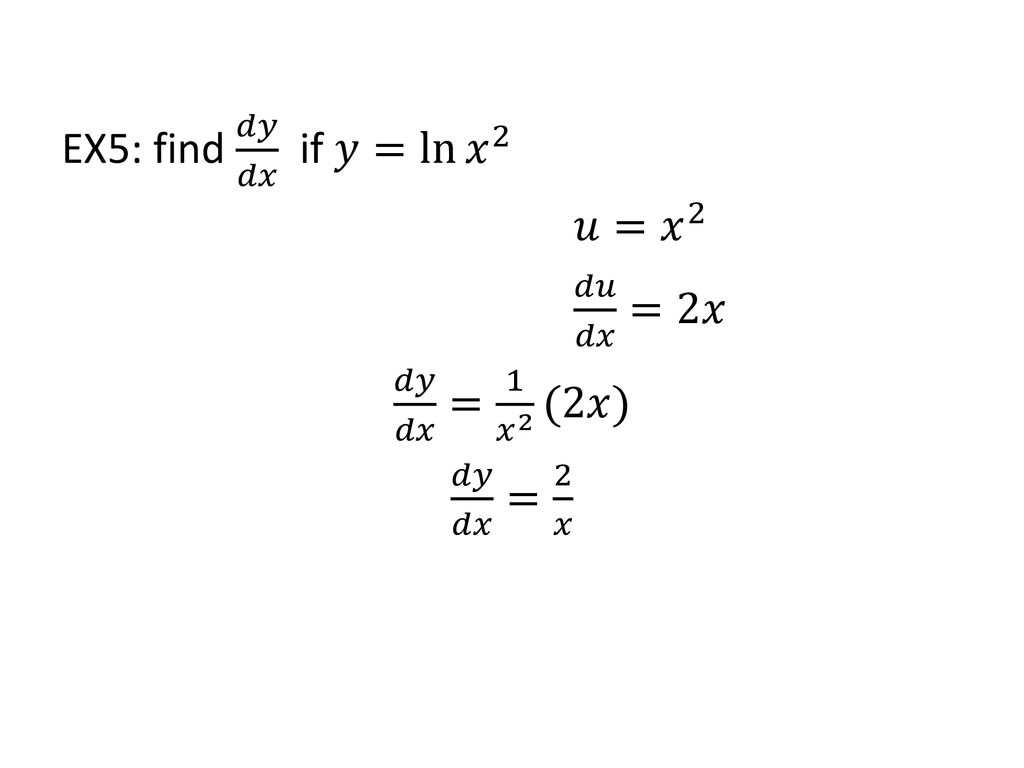



Derivatives Of Ppt Download




Solving The Derivative Of Ln X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Derivative Of Ln X Video Khan Academy
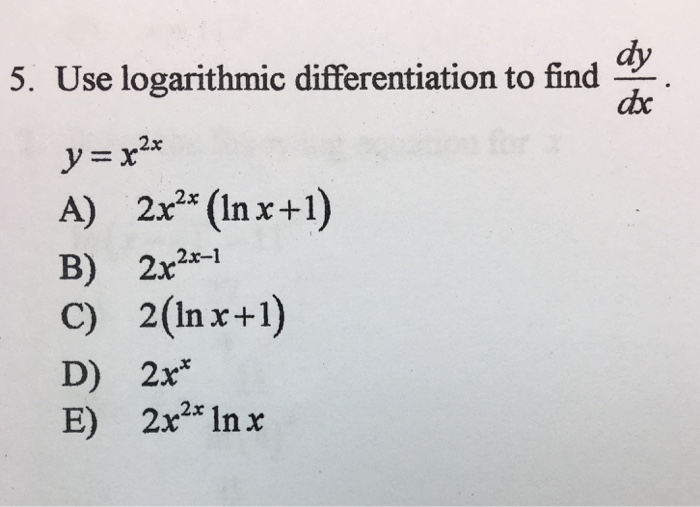



Use Logarithmic Differentiation To Find Dy Dx Y Chegg Com



What Is The Nth Derivative Of Logx Quora



3 8 Implicit Differentiation Calculus Volume 1
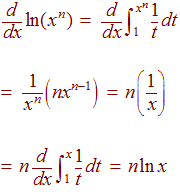



Logs And Derivatives




Derivative Rules



How To Differentiate E 2x Ln X Quora



14 2 Limits And Continuity



5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function


